Japanese Style Acupuncture Therapy
Japanese Acupuncture is a system of health care that has developed over the past 1800 years. The foundation on which it is set is based on the concept of Qi (pronounced chee). Qi is the life force that circulates through all parts of the body via energy channels, called meridians. These meridians may be thought of as similar to the lymphatic or vascular system in the body. Each meridian is responsible for the physical and emotional balance in the body.
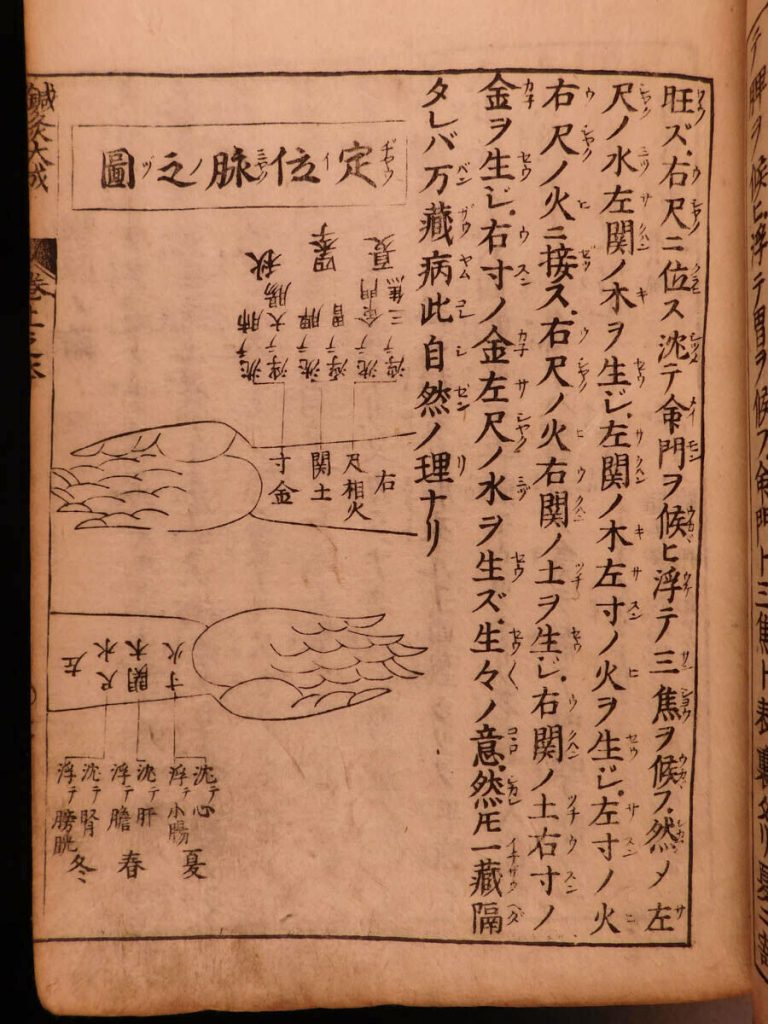
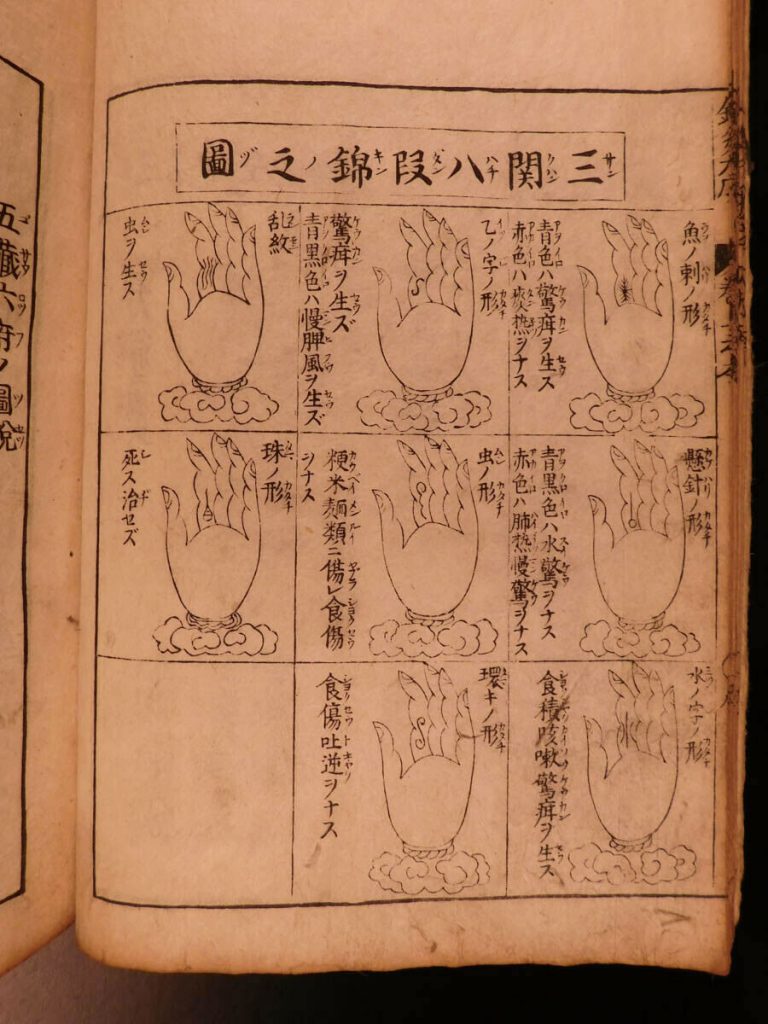
The condition of health in the meridians is reflected in the radial wrist pulse (myaku) and the abdomen (hara).
The abdomen is palpated with light pressure, checking for temperature and texture differences. Different areas of the abdomen correspond to specific meridians and organs. The pulse is palpated at the wrist, checking for speed, depth, and quality. Careful examination includes medical history, medications, lifestyle choices, diet, and exercise. The information gathered from questioning, observing and palpating will factor into the overall diagnosis and state of health of the meridians and organs.
There are points located along the meridians that have specific actions and effects. These points are where the acupuncturist will gather the Qi. Hair-fine, sterile, acupuncture needles are inserted into points along the meridians. Other techniques involve holding, stroking or tapping of a needle or an acupuncture tool at a point. This helps smooth the flow of Qi and restore balance, allowing the body to work at an optimal level of health.
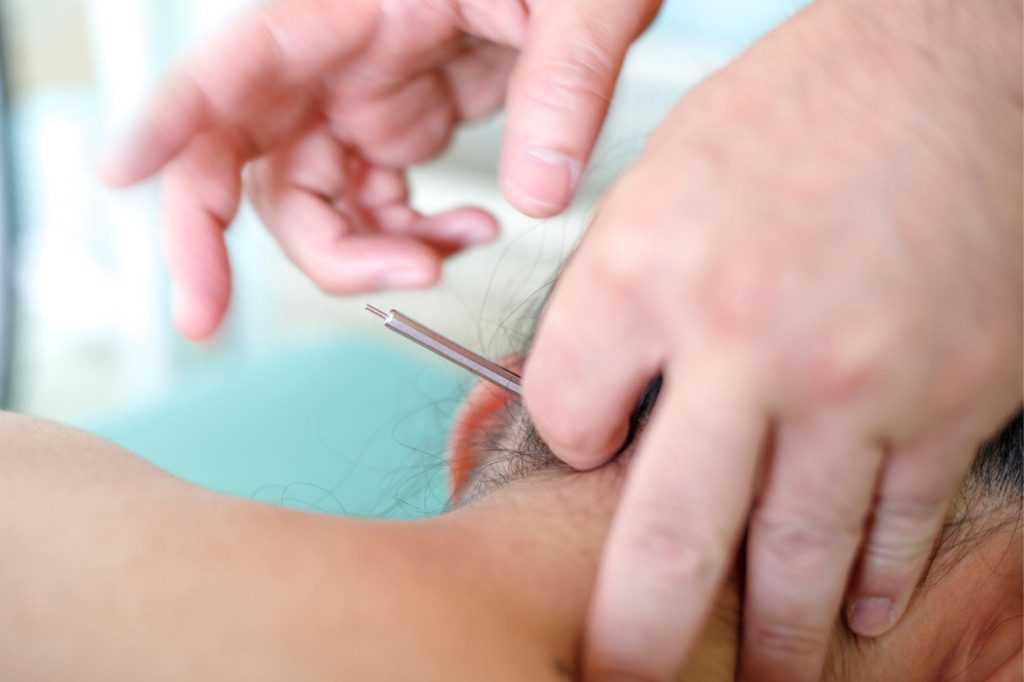
Both the left and right hand are used during a Japanese style acupuncture treatment. The oshide, the technique of holding the acupuncture needle with the left hand is coupled with the right hand or sashide that inserts the needle. The oshide is important in receiving the information felt beneath the needle or on the skin (temperature, texture, etc.). The sashide is important for executing the approach of the needle to the oshide and in manipulating the needle or acupuncture tool for different techniques.